
Greece
Last updated in June 2025
Chapter 1: Higher Education System
1.1. Schematic Diagram of Higher Education System
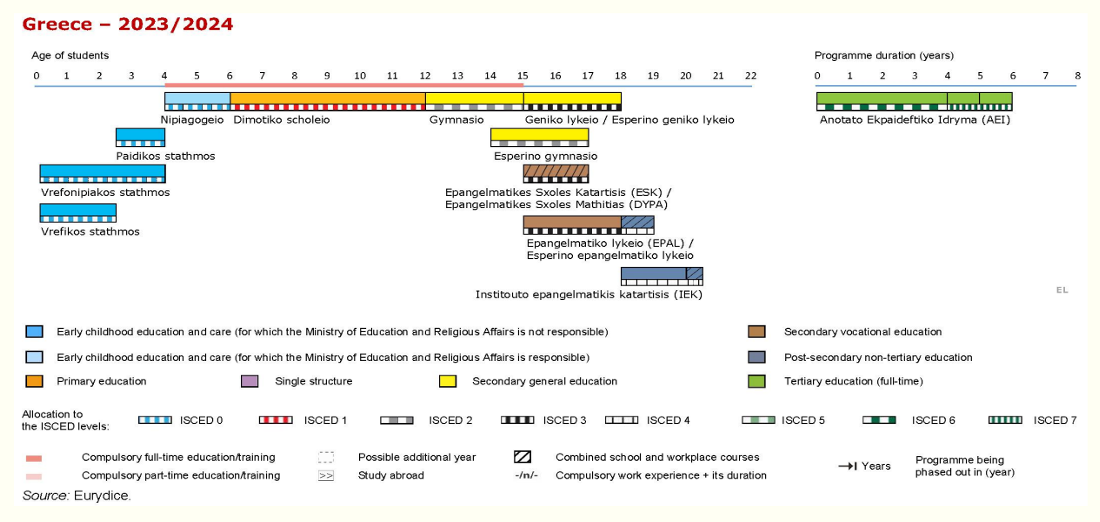
1.2. Description of Higher Education System
Education at university level is provided by institutions which are fully self-governed public law legal persons or non-profit branches of foreign universities (Law 5094/2024). More specifically, these branches of foreign universities can award higher education qualifications and are associated with higher education institutions located and recognised in other Member States of the European Union or in third countries. They are licensed after a specific evaluation procedure by domestic competent authorities, as Non-profit, Non-state institutions of higher education. (The licensing procedure for the first University Legal Εntities is expected to be completed in the following months).
Higher education is the last level of the formal education system. Undergraduate degree programmes take 4 or 5 academic years of full-time study (with the exception of medicine programmes that take 6 years of full-time study).
Postgraduate courses last from one to two years, while doctorates at least 3 years.
Higher Education1 comprises:
The university sector (panepistimio):
- Universities (AEI)
- Technical Universities
- The Athens School of Fine Arts (ASKT).
The technological sector:
- The School of Pedagogical and Technological Education (ASPETE)2.
1Military Education Institutions (ASEI) are equivalent to those of the university sector. They offer equivalent higher education and degrees (l. 3187/2003)
2See Section 1.12
1.3. List of Higher Education Institutions
24 Higher Education Institutions (HEIs), 1 Technological education institution:
https://studyingreece.edu.gr/universities/#Academic_Map
Greek Higher Educational Institutes – ΔΟΑΤΑΠ
1.4. Number of Students in Higher Education
Population of students per type of Higher Education Institution for the Academic year 2023-24: 639.617 (Undergraduate programs of study), of which 299.586 are active.
More data can be found on the Greek Quality Assurance Agency site (www.ethaae.gr)
1.5. Structure of Academic Year
The academic year in the field of higher education regarding undergraduate programmes of study begins on 1 September each year and ends on 31 August of the following year. The Senate of the HEI shall approve the beginning and the end of the academic semesters. By decision of the Senate of the HEI, following a reasoned recommendation of the Assembly of the Department, the duration of the academic semester may be extended if the educational activities were not carried out for reasons of force majeure, in accordance with the respective programme of study and the approved timetable. Regarding postgraduate programmes of study, the start of the academic year is determined on the basis of the Operating Regulation of the respective programme of study.
Every academic year includes two semesters. Every semester includes at least 13 weeks of teaching.
If the assessment method is by final examination, the examinations shall be held after the completion of the academic semester for first cycle programmes of study and by resit after the completion of the academic year. Regarding second and third cycle programmes of study, assessment may be carried out either after the completion of each academic semester or after the completion of the teaching of each course or the completion of each educational activity, as specified on the basis of the Operating Regulation of the respective programme of study.
1.6. National Qualifications Framework (or Similar)
The 8 levels of the Hellenic Qualification Framework cover the full qualification range between Primary and Higher Education. Each level includes a set of skills, competences and knowledge that determines the learning outcomes. The Learning Outcomes constitute the qualifications of the corresponding level.
https://nqf.gov.gr/en/index.php
1.7. Learning Outcomes in Higher Education
| Level | Knowledge | Skills | Competence |
| 6 | Has advanced knowledge of a field of work or study, involving critical understanding of theories and principles. | Possesses advanced skills and has the ability to demonstrate the virtuosity and innovation required to solve complex and unpredictable problems in a specialized field of work or study | Can manage complex technical or professional activities or projects, taking responsibility for decision-making in unpredictable work or study contexts; can assume responsibility for managing the professional development of individuals and groups. |
| 7 | Has highly specialized knowledge, some of which is cutting- edge knowledge in a field of work or study and which is the basis for original thinking; has a critical awareness of knowledge issues in a field and at the interface of different fields. | Holds specialized problem-solving skills required in research and/or innovation in order to develop new knowledge and procedures and to integrate knowledge from different fields. | Can manage and transform work or study contexts that are complex, unpredictable and require new strategic approaches; can take responsibility for contributing to professional knowledge and practices and/or for the performance evaluation of strategy groups. |
| 8 | Has knowledge at the most advanced levels of a field of work or study and at the interface with other fields. | Has acquired very advanced and specialized skills and techniques, including synthesis and evaluation, required to solve critical problems in research and/or innovation for enlarging and redefining existing knowledge or existing professional practice. | Demonstrate substantial authority, innovation, autonomy, scholarly and professional integrity and sustained commitment to the development of new ideas or processes at the forefront of work or study contexts including research. |
Source: HQF Levels (eoppep.gr)
1.8. Admission Requirements to Higher Education
In Greece undergraduate students in all Universities are admitted on the basis of their performance at national level entrance examinations (‘Pan-Hellenic’ exams). These examinations are administered by the Ministry of Education and currently held once a year.
Successful admission to a higher education institution is determined through the combination of a) the candidate’s exam scores b) the candidate’s choices (by order of preference) of desired degree courses and academic institutions, and c) the number of places available in each academic department.
The application and selection procedures for candidates to all undergraduate University programs in Greece are made centrally, through the Ministry of Education, and the number of students for each University and Department is also determined each year by the Ministry of Education.
International Students
International students wishing to study for an undergraduate degree in Greece should start by choosing a course and an institution. Applications are then made in July of each year through the Ministry of Education
Applications and admissions procedures differ for (a) candidates of Greek descent and (b) for EU and non-EU students where neither they nor their parents are of Greek nationality or citizenship.
Source: Applications | Studies | University of Crete (uoc.gr)
1.9. Grading System
Legal framework: The overall Grading System is imposed by law
Student target group: Bachelor and Master
Grade range: 1 to 10; Pass grade 5; other pass grade levels 6-7
Description of the grading system: The grading system is determined according to the Operating Regulation of the respective programme of study.
1.10. Tuition Fee System for International Students
Tuition fees are charged by HEIs:
- to international students for undergraduate courses taught in a foreign language
- to postgraduate courses
- summer and winter short courses
- lifelong learning courses
1.11. Graduation Requirements and/or Qualification Awarding Requirements
ΗEIs offer study programmes which are classified in three cycles.
The first cycle refers to undergraduate programs of study which award at least 240 ECTS and have a minimum duration of 8 academic semesters. The successful completion of an undergraduate programme of study leads to level 6 of the National and European Qualifications Framework.
The second cycle includes postgraduate programmes of study which award at least 60 ECTS and have a minimum duration of 2 academic semesters. The successful completion of a postgraduate programme of study leads to level 7 of the National and European Qualifications Framework.
Some graduate programmes lead directly to a second-cycle degree. According to l. 4957/2022, the successful completion of a first-cycle study in these programmes leads to the award of a single and integrated master’s degree in the specialty of the Department and the degree corresponds to a level seven (7) degree in accordance with both the National and European Qualifications Framework.
The third cycle includes doctorate programmes of study which have a minimum duration of 3 academic years. The successful completion of a doctorate programme of study leads to level 8 of the National and European Qualifications Framework.
1.12. Relevant Current and Prospective Reforms in Higher Education
The School of Pedagogical and Technological Education is in the process of merging with the Faculty of Education Studies at the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, where it will be renamed “Pedagogical Department of Educational Engineering”.
Chapter 2: Quality Assurance in Higher Education
2.1. Quality Assurance Body in Higher Education
The Hellenic Authority for Higher Education (HAHE) was established in 2020 as the successor to Greece’s Quality Assurance and Accreditation Agency, which had operated since 2006. The Authority is an independent body with full administrative and operational autonomy and a legal supervision by the Minister of Education. It is governed by its President and Supreme Council. Quality assurance is managed by the Evaluation and Accreditation Council.
HAHE is a member of the European Association for Quality Assurance in Higher Education (ENQA) and of the European Quality Assurance Registry (EQAR).
2.2. Quality Assurance System
| Programme | Institution | |
| Voluntary | ||
| Compulsory | X | X |
| Regularity | 5 years | 5 years |
| External | X | X |
| Internal | X | X |
Further explanation:
Accreditation includes:
a) Internal evaluation carried out by the Institution through its Quality Assurance Unit (QAU/MODIP) and
b) External evaluation by a Panel of Independent Experts.
The process is primarily centered on the quality and effectiveness of the Internal Quality Assurance System(IQAS)/Study Programme(SP), by shifting to some extent the focus away from evaluating “input” to evaluating qualitative outcomes (“output”), and in particular to achieving the objectives of the IQAS/SP.
The Accreditation process includes the following steps:
- Accreditation Proposal of an IQAS/SP to be submitted to HAHE by the Quality Assurance Unit (QAU) of the Institution;
- Review by a Panel of Independent Experts (External Evaluation & Accreditation Panel – EEAP) including a site visit to the Institution;
- An Accreditation Report resulting from the accreditation process drafted by the Panel to be submitted to HAHE;
- Adopting and publishing the HAHE Accreditation Decision;
- Consistent follow-up of the IQAS/SP operation by the Institution’s QAU.
According to the appeals procedure provided for, the Institution may question the formal outcomes of the IQAS/SP accreditation process, where it can demonstrate that the outcome is not based on sound evidence, that criteria have not been correctly applied or that the procedures have not been consistently implemented.
If the Institution wishes to appeal the decision of the EAC or the judgement by the EEAP that it is not compliant with the HAHE Standards, the HAHE Appeals and Complaints Committee will hear the appeal.
Source: Guidelines for Accreditation (ethaae.gr)
2.3. Programme Authorisation and Quality Assurance
All existing programs of study of Greek HEIs are considered accredited by the Hellenic Authority for Higher Education (H.A.H.E), because according to the provisions of law 4653/2020, art. 8, all programs of study have to be accredited before they begin to operate. Foreign quality assurance agencies may accredit programs of study or conduct external quality assurance of a HEI, provided they get authorization by the HAHE.
More information about accreditation of Higher Education Institutions and programs of study can be found on the HAHE site: www.ethaae.gr
Chapter 3: Credit System in Higher Education
3.1. Description of Credit System
Higher education institutions in Greece operate a full-fledged credit system based on ECTS (European Credit Transfer and accumulation System).
3.2. Credit Transfer System(s)
European Credit Transfer and accumulation System (ECTS)
3.3. Additional Information
3.4. Is Application of Credit System in Higher Education Institutions Mandatory?
Yes.
3.5. Number of Credits per Academic Year/Semester
Please see 1.11
3.6. Number of Credits per Higher Education Cycle
Please see 1.11
3.7. Description of Credit Unit
3.8. Link between Learning Outcomes and Credits