Malta
Last updated in 2020
Chapter 1: Higher Education System
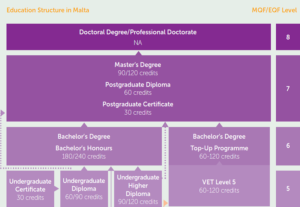
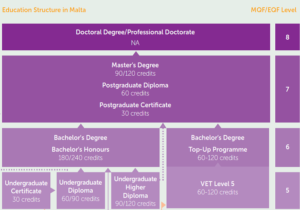
1.1. Schematic Diagram of the Higher Education System
Note: Undergraduate refers to the academic stream
https://ncfhe.gov.mt/en/Documents/Referencing%20Report/Referencing%20Report%202016.pdf
1.2. Description of Higher Education System
The three main higher education institutions in Malta which are state funded are the
- University of Malta
- Malta College of Arts, Science and Technology
- Institute of Tourism Studies
Apart from these there are several private higher education institutions which offer courses from Level 5 to Level 8.
The diagram in section 1.1 shows the number of credits for each qualification. The number of credits per academic year on a full-time basis, assigned at Levels 5-8 falls within the Bologna Process which specifies that the associated workload of a full-time academic year, or its equivalent, is that of 60 credits. Hence a Bachelor’s degree consisting of 180 credits is of 3 years duration. First cycle bachelor’s degrees vary in duration between three to four years depending on the specialization and the area of study.
https://ncfhe.gov.mt/en/Documents/Referencing%20Report/Referencing%20Report%202016.pdf
1.3. Number of Higher Education Institutions
1.4. Number of Students in Higher Education
Please refer to the official publication below. Data is currently being collected for the period 2019-2020
https://ncfhe.gov.mt/en/services/Documents/Research/NCFHE%20Statistics%20Report%202015-2016_synopsis.pdf
1.5. Structure of Academic Year
The academic year starts in October and ends in June. There are two semesters, from October to January and from February to June. Examination period is held at the end of January and during the whole month of June.
The above structure is related to the publicly funded providers which the private institutions mostly follow.
1.6. National Qualifications Framework (or Similar)
| The Malta Qualifications Framework (MQF) | ||
|
8
|
Doctoral Degree
|
|
|
7
|
Master’s Degree
Post-graduate Diploma
Post-graduate Certificate
|
|
|
6
|
Bachelor’s Degree
|
|
|
5
|
Undergraduate Diploma
Undergraduate Certificate
|
VET Higher Diploma
Foundation Degree
|
|
4
|
Matriculation Certificate
Advanced Level
Intermediate Level
|
VET Diploma (iv)
|
|
3
|
General Education
SEC Grade 1-5
|
VET Level 3 (iii)
|
|
2
|
General Education
Level 2
SEC Grade 6-7
|
VET Level (ii)
|
|
1
|
General Education
Level 1
School Leaving Certificate
|
VET Level (i)
|
|
B
|
Introductory Level B*
|
|
|
A
|
Introductory Level A*
|
|
|
*These are not yet included in legislation
Annotations
|
||
1.7. Learning Outcomes in Higher Education
Qualification levels on the Malta Qualifications Framework are specified through the Level Descriptors. These descriptors are stated in terms of knowledge, skills and competences and the consequent learning outcomes achieved. Subsidiary Legislation 327.431 ‘Malta Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning Regulations’ establishes that qualifications forming part of the MQF shall be based on learning outcomes, and as such shall be expressed in terms of knowledge, skills and competences corresponding to the respective level descriptors.
Accreditation of HE curricula is based on learning outcomes which determine the level rating on the Malta National Qualifications Framework.
1.8. Admission Requirements to Higher Education
Whilst there is no national legislation about admission requirements, usually providers of HE follow the below entry requirements of publicly funded HE institutions which are
- the Matriculation Certificate and a pass at grade 5 or better in the Secondary Education Certificate (SEC) examinations in English Language, Maltese and Mathematics. A non-Maltese applicant may be allowed to offer another language as approved by the Admissions Board instead of Maltese. The other language cannot be English, and applicants whose mother tongue is English, shall be required to offer a language other than English instead of Maltese.
The Matriculation Certificate comprises six subjects and is awarded if students obtain a certain number of points including passes in a language, a science subject and a humanistic subject as well as a pass in a subject entitled ‘Systems of Knowledge’. Two of the six subjects must be at Advanced Level, three others at Intermediate Level and Systems of Knowledge. - a student who has pursued secondary education outside Malta, the HE institutions would accept comparable qualifications, provided that the required mix of subjects and levels would is comparable to the Matriculation Certificate.
- Applicants who hold dual citizenship, or who become naturalised Maltese citizens, are required to be in possession of a pass in Maltese at SEC level for entry to a course at the University of Malta (UM). Foreign qualifications are independently evaluated by UM to assess the comparability against national framework levels.
- At Malta College of Arts Science and Technology (MCAST) the general entry requirements into higher level programmes is usually two subjects at Advanced Level and a number of subjects at Ordinary level, or equivalent. This may include the MCAST-BTEC (Malta College of Arts Science and Technology – Business and Technology Education Council) National Diploma in the main subject applied for. This permits for progression into higher level studies. Applicants from other EU member states as well as applicants from outside of the EU may apply to join programmes run by MCAST. It is the responsibility of such applicants to provide an equivalence certificate from the national authority.
1.9. Grading System
Each Higher Education System has its own grading system.
1.10. Tuition Fee System for International Students
Different tuition fees f or international students apply in publicly funded HEI or Universities discriminating between EU/EEA citizens and non EU/EEA citizens where the later pay higher than the former for all courses.
- University of Malta fees: https://www.um.edu.mt/international/students/tuitionfees
- Malta College for Arts Science and Technology fees: https://www.mcast.edu.mt/fee-payments-for-non-eu-candidates/
- Institute for Tourism Studies fees: https://its.edu.mt/courses-admission/how-to-apply/tariff-and-fees.html
1.11. Graduation Requirements and/or Qualification Awarding Requirements
- A minimum of 180 ECTS are required to obtain a Bachelor’s degree
- A minimum of 30 ECTS are required to obtain a Postgraduate Certificate
- A minimum of 60 ECTS are required to obtain a Postgraduate Diploma
- A minimum of 90 ECTS are required to obtain a Master’s degree
1.12. Relevant Current and Prospective Reforms in Higher Education
In February 2020 the Parliament approved an Act to regulate further and higher educational institutions and education providers in Malta and other ancillary matters. The Act aims to establish the National Commission for Further and Higher Education in an Authority which is more independent from the Ministry of Education.
Chapter 2: Quality Assurance in Higher Education
2.1. Quality Assurance Body in Higher Education
The National Commission for Further and Higher Education (NCFHE) is the competent authority in Malta responsible for quality assurance of the HE. For the purposes of its accreditation and external quality assurance functions, the Commission is independent from government, from providers as well as from business, industry and professional associations in all their operations and decisions.
In accordance with article 69(10) of the Education Act, Chap. 327 of the Laws of Malta, the Commission shall establish a Quality Assurance Committee to carry out its licensing, accreditation and quality assurance functions under these regulations. Decisions taken by the Quality Assurance Committee require adoption by the Commission for their validity and enforcement.
2.2. Quality Assurance System
|
|
Study programme
|
Institution
|
|
Voluntary
|
||
|
Compulsory
|
X | X |
|
Regularity
|
|
5 years
|
|
External
|
X | X |
|
Internal
|
X | X |
|
Further information: Please refer to Subsidiary Legislation 327.433
|
||
2.3. Link Programme Authorisation with Quality Assurance
The licensing of Further and Higher education institutions is subject to periodic external quality assurance auditing by NCFHE. External quality assurance audits can focus either on programme quality audit or provider quality audit. The implementation of this regulatory framework is important as it gives national qualifications credibility on both national and international level.
The quality of the Qualifications and Awards accredited depends on the quality of the provision of education and training by the Further and Higher Education providers in Malta. In 2015, NCFHE established the National Quality Assurance Framework for Further and Higher Education institutions in Malta. The accreditation of Qualifications and Awards is based on the implementation of this National Quality Assurance framework within the education and training providers obtaining accreditation.
Hereunder is link to accredited courses by NCFHE:
https://ncfhe.gov.mt/en/register/Pages/register.aspx
Chapter 3: Credit System in Higher Education
3.1. Description of Credit System
All courses accredited by NCFHE are assigned a number of credits based on their total learning workload. The University of Malta has fully implemented a credit system based on ECTS for a number of years. The Malta College for Arts, Science and Technology, the main VET provider also uses credits (ECVET for levels 1-4 and ECTS for Level 5 and higher). The Institute for Tourism Studies also uses ECVET credits as the basis for programme design and planning. All courses accredited by NCFHE are included in the national register for accredited courses with identifiable credit points.
3.2. Credit Transfer System(s)
ECTS – European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System.
3.3. Additional Information
Not applicable.
3.4. Is Application of Credit System in Higher Education Institutions Mandatory?
Yes.
3.5. Number of Credits per Academic Year/Semester
Qualifications at Levels 2-7 on the Malta Qualifications Framework are designed on a maximum of 60 credits per academic year where delivery is undertaken on a full-time basis. This amounts to 1500 hours (60 credits x 25 hours of learning per credit) per academic year. At MQF Level 1, the maximum number of credits per academic year is 40 credits (40 credits x 25 hours of learning per credit) per academic year. The number of credits per academic year on a full-time basis, assigned at Levels 5-8 falls within the Bologna Process which specifies that the associated workload of a full-time academic year, or its equivalent, is that of 60 credits.
3.7. Description of Credit Unit
In Malta, 1 credit is equal to 25 hours of teaching and learning including a minimum of 5 hours of contact teaching and learning hours.
MQF Level 1: The maximum number of credits per full-time year is 40, equivalent to 1,000 hours (40 credits x 25 hours per ECTS).
MQF Levels 2-7: The maximum number of credits per full-time year is 60, equivalent to 1,500 hours
(60 credits x 25 hours per ECTS).
The number of credits allocated per year for full-time study at Levels 5 to 8 aligns with the Bologna
Process, specifying a full-time year’s workload as equivalent to 60 credits. The MFHEA addresses requests for part-time programmes, which may extend outside the academic year, on a case-by-case basis.
Credits are awarded based on the achievement of defined learning outcomes, and qualifications must meet minimum credit thresholds as prescribed for each MQF level.
More information can be found here: Referencing Report – Malta Further & Higher Education Authority
And the most updated version is available here:
MFHEA_A4-Referencing-Report-APRIL-2025-2_compressed.pdf
3.8. Link between Learning Outcomes and Credits
In Malta, learning outcomes and credits are closely interrelated within the National Qualifications System. The Malta Qualifications Framework (MQF) uses level descriptors based on learning outcomes, which define what a learner is expected to know, understand, and be able to do upon completing a programme. These learning outcomes – structured around knowledge, skills, and competences – form the basis for assigning credits.
Each credit reflects the volume of learning required to achieve specific learning outcomes, measured in terms of total workload. This alignment ensures that credits are based on the achievement of meaningful educational objectives, consistent with European standards and referenced to the European Qualifications Framework (EQF).
For further information:
https://mfhea.mt/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/MFHEA_A4-Referencing-Report-APRIL-2025_compressed.pdf