
Cyprus
Last updated in 2023
Chapter 1: Higher Education System
Section 1.1.: Schematic Description of the Higher Education System
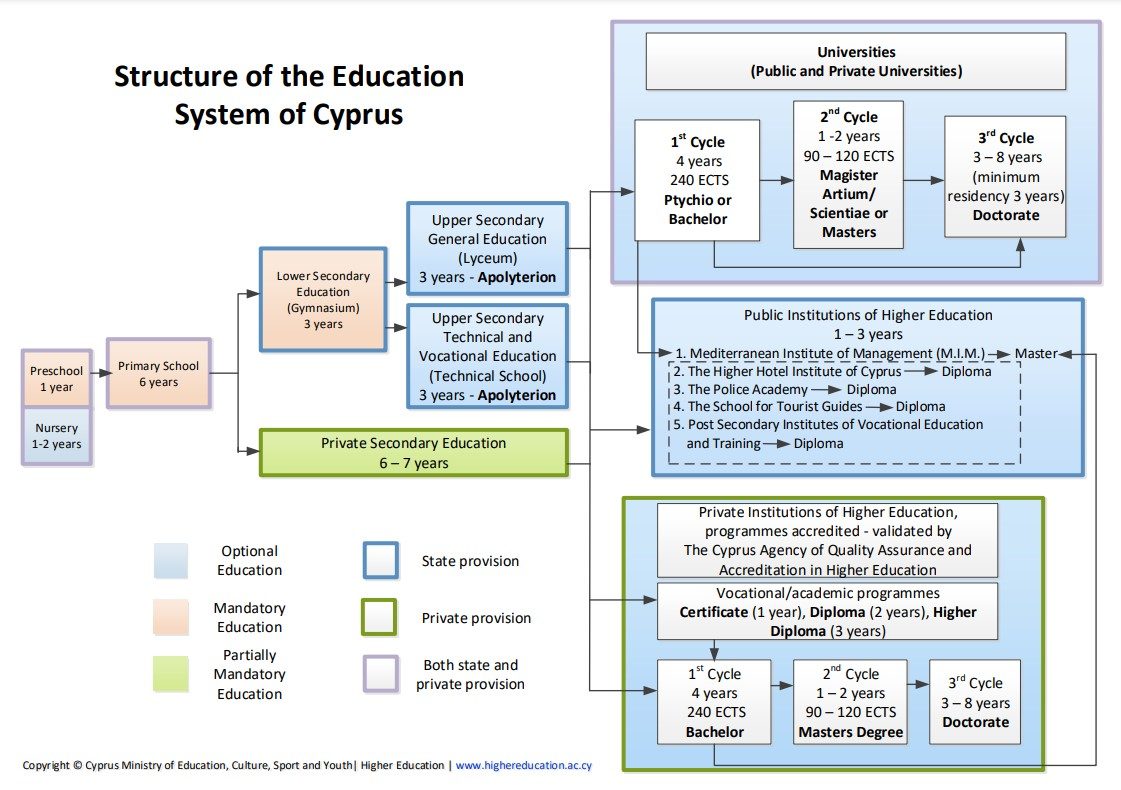
Section 1.2: Description of Higher Education System
Cyprus places a great deal of value on Higher Education. The country has one of the highest tertiary educational attainment rate in the EU with 58.3 % of 30-34 year olds having a Higher Education degree in 2021 (EU average: 41.2 %).
Cyprus’ Higher Education sector is still comparatively young (the country’s first University – The University of Cyprus – was founded in 1989 and became operational in 1992), but it has nonetheless expanded substantially over the past three decades. The Higher Education System in Cyprus consists of Universities and Institutions of Higher Education, both Public and Private.
Some of the Institutions of Higher Education, offer short term programmes, mostly for specific professions, that provide students with Certificates (1 year), Diplomas (2 years), and Higher Diplomas (3 years). Many courses include periods of placement at the workforce environment. There is also a significant number of Institutions of Higher Education that along with Universities, provide Bachelor and Master Degrees. Two private Institutions, namely the Cyprus Institute and the Cyprus Institute of Neurology and Genetics, provide PhD Programs. The Open University of Cyprus is the country’s only Public University devoted entirely to open and distance education and lifelong learning. Distance learning is also provided as an option from the majority of the Institutions of Higher Education, especially after the emergency measures that Cyprus Government implemented towards the interception of the pandemic COVID-19.
Cyprus Universities, both public and private, offer Academic and Professional Bachelor Degrees of 4-year duration (240 ECTS[1]). A Bachelor Degree is a stepping stone for studies at a Master’s level. Master programmes are characterised by the integration of education and research. Students are given the choice to fulfil the programs requirements either by succeeding in a specific number of modules (total 120 ECTS) or by combining selected modules along with a Master’s dissertation.
Doctorate degree is the highest level of an academic degree provided by Cyprus Universities and Institutions of Higher Education. It is based on an original research project and aims to contribute in an innovate way to the existing international knowledge in any subject area
Section 1.3: Number of Higher Education Institutions
Section 1.3: Number of Students in Higher Education
Table 1: Population of Students per Type of Higher Education Institution for the Academic Year 2021-2022
| 2021-2022 | ||||
| Type of Higher Educational Institution | Students | |||
| Cyprus | European Union | Rest of the World | Total | |
| Public and Private Universities | 18190 | 21176 | 3809 | 43175 |
| Public and Private Institutions of Higher Education | 9873 | 813 | 7361 | 18047 |
| Total | 28063 | 21989 | 11170 | 61222 |
Table 2: Students enrolment per program of study for the Academic Year 2021-2022
|
2021-2022 |
||||||
|
Enrolments |
Outgoing mobility | |||||
| Cypriot students | European Union students | International students | Total | |||
| Public and Private Institutions of Tertiary Education | Programs of studies (1-3 years) Certificate, Diploma, Higher Diploma | 3674 | 271 | 1337 | 5282 | 42 |
| Bachelor | 3710 | 388 | 5440 | 9538 | 56 | |
| Master | 2371 | 98 | 542 | 3011 | 0 | |
| PhD | 118 | 56 | 42 | 216 | 2 | |
| Total | 9873 | 813 | 7361 | 18047 | 100 | |
| Public and Private Universities | Bachelor | 12526 | 5525 | 2774 | 20825 | 156 |
| Master | 4425 | 14757 | 904 | 20086 | 3 | |
| PhD | 1239 | 880 | 131 | 2250 | 1 | |
| Total | 18190 | 21162 | 3809 | 43161 | 160 | |
| Total Universities and Institutions of Tertiary Education | 28063 | 21975 | 11170 | 61208 | 260* | |
Section 1.5: Structure of Academic Year
The academic year consists of two semesters as follows:
Winter Semester: September – January
Spring Semester: February – June
Each semester ends with an examination period and for the majority of HEIs there is also a second chance examination period in August-September.
Section 1.6: National Qualifications Framework (or Similar)
The Cyprus National Qualifications Framework (CyQF) has been in alignment with the European Qualifications Framework and is structured as follows:
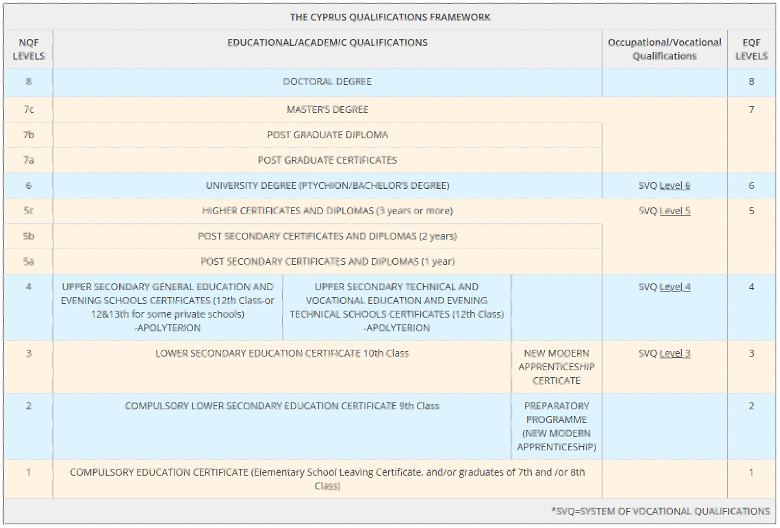
http://www.cyqf.gov.cy/index.php/en/diagram
Section 1.7: Learning Outcomes in Higher Education
Cyprus does not yet have a National Framework for validating non-formal and informal learning. However, it is currently under development, through a project, partially funded by the European Structural and Investment (ESI) Funds. This project, which started at the beginning of 2018, has supported a mapping study of the current situation in Cyprus and a National Action Plan, setting up a validation mechanism for the validation of non-formal and informal learning.
The National Action Plan was discussed with stakeholders during the first half of 2018 and was completed in May 2018. Currently there is an ongoing pilot implementation of the plan, focusing on adult education, youth and volunteering. The validation process will entail five stages: information-individualized counselling; identification; recognition of learning outcomes; assessment of learning outcomes; and certification.
CYPRUS European inventory on NQF 2018
http://www.cedefop.europa.eu/files/cyprus_-_european_inventory_on_nqf_2018.pdf
Section 1.8:Admission Requirements to Higher Education
| Type of Educational Institute |
Students Admission Requirements |
|
| Public Universities | Undergraduate Studies | The entrance for undergraduate studies in the two conventional Public Universities of Cyprus is attained upon success at the Pancyprian Exams which are organized centrally by the MOEC. Eligible to participate at the Pancyprian Exams are holders of a Cypriot Secondary School Leaving Certificate (Apolyterion) or an equivalent foreign qualification verified by an Accreditation Council/Body of the country of origin.
The Open University of Cyprus offers Bachelor Degrees only in Greek. |
| Postgraduate Studies | Applicants must have a University degree awarded by an accredited Institution of HE in the country where it operates, or a degree evaluated as equivalent to a University degree by the Cyprus Council for the Recognition of Higher Education Qualifications (KY.S.A.T.S.). In general, academic Bachelor degrees give access to Master degrees and Master degrees give access to PhD programmes.
For admission to some postgraduate programmes, candidates are required to have proficiency in English that can be demonstrated through internationally certificates of English Language Proficiency (e.g. IGCSE, IELTS, TOEFL). For the majority of programmes of study applicants for PhD Degree must be holders of a Master Degree. |
|
| Private Universities | Undergraduate Studies | The general admission requirement for entry to an undergraduate programme of study is a recognised Secondary School Leaving Certificate or equivalent. Some programmes may have additional requirements, in which case, they are specified separately under the relevant programme requirements. English is often the main language of instruction at Private Universities. Students may be required either to take an English test before registering for classes, or to prove that they have passed an internationally recognised English exam which indicates their level of English proficiency. |
| Postgraduate Studies | The minimum requirement for admission into a Postgraduate Study Programme (Master degree) is a Bachelor Degree from an accredited Institute of HE. In addition to the minimum requirements, special admission requirements may apply for some Departments. For the majority of programmes of study applicants for a PhD Degree must be holders of a Master Degree. | |
| Public and Private Institutions of Higher Education | Post-Secondary Certificates and Diplomas (1, 2, 3 years duration) | Admission requirements may vary depending on the Institutions’ requirements. However, the following two are necessary:
– Qualified Secondary School Leaving Certificate. – Proof of proficiency in English language. |
| Undergraduate Studies | ||
| Postgraduate Studies (where applicable) | Basic admission requirements:
-University degree or equivalent qualification in any subject. -Master degree when applying to PhD programmes. -Proof of proficiency in English language for programmes offered in English. |
|
Section 1.9: Grading System
In general, for Bachelor and Master degrees the Grading system ranges between 0 – 10 with an interval of half points (7.5, 8.5 etc.). Grade 5 is the pass mark in an overall average of assignments, tests and final examinations.
Section 1.10: Tuition Fee System for International Students
| Type of Educational Institute |
Tuition fees |
|
| Public Universities | Undergraduate Studies | EU students €3417,20/yearly (FREE – paid by the Republic of Cyprus)
Non EU students €6868,41/yearly |
| Postgraduate Studies | €4100-€10250/ in total | |
| Private Universities | Undergraduate and Postgraduate Studies | Tuitions and fees are approved by the Ministry of Education and Culture of Cyprus and are announced at the Institutions’ official websites. Nevertheless, the Universities reserve the right to change the fees and charges where appropriate
€9000-€25000* *For the field of Medicine |
| Public and Private Institutions of Higher Education | Post-Secondary Certificates and Diplomas (1, 2, 3 years) | In general tuition fees vary depending on the Institutions’ regulations and programs offered.
Foreign students ≈ €3500-€6500/yearly |
| Undergraduate Studies | Foreign students ≈ €4000-€7500/yearly | |
| Postgraduate Studies (where applicable) | Foreign students ≈ €5500-€7500/in total | |
Section 1.11: Graduation Requirements and/or Qualification Awarding Requirements
There are specific graduation requirements, which are analytically specified in each Institution of Higher Education’s Prospectus.
Section 1.12: Relevant Current and Prospective Reforms in Higher Education
There are no relevant current/prospective reforms in HE at present.
Chapter 2: Quality Assurance in Higher Education
Section 2.1: Quality Assurance Body in Higher Education
The Cyprus Agency of Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Higher Education (CYQAA), is responsible to ensure the quality of Higher Education in Cyprus and to support, through the procedures provided by the relevant legislation for the continuous improvement and upgrading of Higher Education Institutions (HEI) and their programs of study.
Additionally, CYQAA has, according to the Law, extended competencies amongst which are the following:
- Institutional, Departmental and Programmatic Evaluation and Accreditation of Higher Education.
- Quality Assurance in Higher Education on the basis of the European Standards.
- The Evaluation and Accreditation of cross-border forms of education, offered by local Institutions of HE in member states or third countries.
- Assessment of the conditions for the provision of cross-border education from foreign Institutions of HE in Cyprus
- Assessment of inter-institutional cooperation of HEI.
- The provision of information of Quality Assurance in Higher Education.
With the cooperation of HEI, CYQAA will be a major contributor towards the effort for the establishment of Cyprus as district Educational and Research Center, in accordance to the standards and guidelines provided by the European Network for Quality Assurance (ENQA). CYQAA is a full member of the European Network of Quality Assurance (ENQA) and a full member of the International Network for Quality Assurance and Accreditation Higher Education (INQAAHE). It is also included on the European Network of Quality Assurance Register (EQAR), and is recognized by the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME).
The lists of all recognized Institutions of Higher Education and of the accredited programs of study as well as evaluation for each HEI, are published in the CYQAA’s website: Home (dipae.ac.cy). Moreover, CYQAA’s external quality assurance results can be found at EQAR’s database, DEQAR: Database of External Quality Assurance Results – EQAR
Section 2.2: Quality Assurance System
| Study programme | Institution | Further explanation | ||
| Voluntary
Please tick. |
||||
| Compulsory
Please tick. |
√ | √ | ||
| Regularity (years)
Please indicate the number of years |
5 years | 5 years | ||
| External
Please tick. |
√ | √ | ||
| Internal
Please tick. |
√ | √ | ||
| Further information:
All Higher Education Institutions are obliged by the relevant laws to have an Internal Evaluation Committee which is responsible to conduct a General Evaluation Report for the Institution, every three years. CYQAA has the authority to require such a report on an annual basis. Every 5 years CYQAA goes through an external evaluation process that refers to Institutional, Departmental or Program of Study Evaluation. |
||||
Section 2.3: Link Programme Authorisation with Quality Assurance
On the basis of the judgments of CYQAA, Higher Education programmes are recognized and students receive a legally recognized degree.
The lists of all recognized Institutions of Higher Education and of the accredited programs of study as well as evaluation results for each HEI, are published on the CYQAA’s website.
http://www.dipae.ac.cy/index.php/en/axiologisi/pistopoiimena-programmata
Chapter 3: Credit System in Higher Education
Section 3.1: Description of Credit System
(European Credit Transfer and accumulation System). One ECTS represents 25 to 30 hours of a student’s workload. Courses are often a combination of compulsory and non-compulsory thematic units for which students may enrol according to their own preferences and timetable, with due consideration for the semester system and evaluations. They can opt for a traditional course of 60 ECTS credits per year, a half-time course or an individual course adjusted to their specific needs.
Link ECTS:
http://ec.europa.eu/education/ects/users-guide/introduction_en.htm#ectsTop
Section 3.2: Credit Transfer System(s)
Select which credit transfer system(s) are used in your country:
-
ECTS – European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System.
Section 3.3: Application of Credit System in Higher Education Institutions Obligatory?
Yes.
Section 3.4: Number of Credits per Academic Year/Semester
The number of credits per standard academic year is 60 ECTS (30 ECTS/semester).
Section 3.5: Number of Credits per Higher Education Cycle (linked to qualification framework)
Section 3.6: Definition/ Description of Credit Unit
Section 3.7: Link between Learning Outcomes and Credits
A student is awarded credits upon achievement of the defined learning outcomes related to the educational unit/course. Learning outcomes (ECTS-definition) are statements of what the individual knows, understands and is able to do on completion of the learning process. The achievement of learning outcomes has to be assessed through procedures based on clear and transparent criteria.
Learning outcomes are attributed to individual educational components and to programmes as a whole. They are also used in European and National Qualifications Frameworks to describe the level of the individual qualification
Section 3.8: Credit transfer system(s) (open question)