Singapore
Last updated in November 2025
Chapter 1: Higher Education System
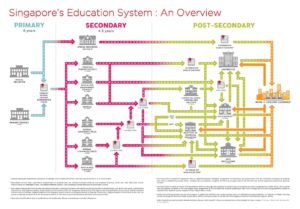
1.1. Schematic Diagram of the Higher Education System
Source: https://www.moe.gov.sg/-/media/files/post-secondary/post-secondary-school-booklet-2021.pdf
1.2 Description of Higher Education System
Institute of Technical Education (ITE)
Students may apply to ITE’s full-time programmes, including Higher National ITE Certification (Nitec) courses, Technical Diplomas and Work-Study Diplomas. In 2022, ITE rolled out the enhanced curricular structure to streamline Nitec and Higher Nitec programmes into a three-year programme. Under these enhanced curricula, students with Singapore-Cambridge Secondary Education Certificate (SEC) will be admitted into a Higher Nitec course, differentiated by duration of enrolment. Most students will be enrolled in 3-year Higher Nitec courses, while those who are eligible could enrol in the 2-year Higher Nitec accelerated curriculum. ITE graduates who wish to further their education may be considered for admission to the polytechnics, as well as ITE’s diploma programmes, based on their Higher Nitec qualifications.
ITE also offers part-time Nitec, Higher Nitec, Specialist Nitec and ITE Skills Certificate (ISC) courses. They are offered in modular form, giving participants the flexibility to sign up for training based on their needs. In addition, ITE offers the Work-Study Diplomas (WSDips) to both fresh and in-employment ITE graduates.
Polytechnics
The Polytechnics offer full-time diploma courses which typically admit students who sit for predominantly G3 subjects at the SEC, and ITE’s Higher Nitec qualifications. Eligible students who sit for predominantly G2 and/or G3 subjects at SEC may also apply for entry to the Polytechnics via the Polytechnic Foundation Programme, which offers a practice-oriented curriculum to prepare them for polytechnic diploma courses. The Polytechnics also admit working adults with relevant work experience. Polytechnic graduates who wish to further their studies may be considered for admission to the universities based on their diploma qualification.
The Polytechnics also offer part-time programmes at diploma and post-diploma level designed for adult learners who want to deepen their knowledge and skills across a range of disciplines and industries.
- Part-time diploma courses are designed to be modular and more compact than full-time diploma courses, to provide more flexible and accessible upgrading opportunities for adults with working experience.
- Post-diploma courses cater to working professionals who are diploma or degree holders. They are modular, shorter in duration than diploma courses, and mostly designed for part-time study. These include the Advanced Diploma and Specialist Diploma courses that cater to adults seeking to deepen their skills and knowledge in the field they are trained or practising in, and Diploma (Conversion) courses that cater to adults seeking training in a different discipline so as to facilitate career switches.
Autonomous Universities (AUs)
Typically, an undergraduate degree takes three to four years to complete, for students who are enrolled full-time in the AUs. Students can also pursue postgraduate or continuing education courses of varying length, and will be awarded qualifications such as postgraduate degrees, graduate diplomas, or certificates of course completion.
University of Arts Singapore (UAS)
UAS is Singapore’s first government-supported private university of the arts, formed as an alliance between the constituent colleges, LASALLE College of the Arts (LASALLE) and Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts (NAFA), and a new central entity, UAS Ltd. Within the alliance, LASALLE and NAFA remain as separate legal entities with their own identities and heritage, and continue to offer their own programmes. UAS Ltd. leads and provides strategic direction to the university. It will also validate, confer and award degrees offered by LASALLE and NAFA. The Art Institutions (AIs), LASALLE and NAFA, offer government-funded diploma programmes in the creative arts, in addition to degrees under UAS. The diploma programmes require three years of study, while the degree programmes can be completed in two years if the student has prior relevant experience. For those students without sufficient experience, the degree programmes require three years of study. Separately, NAFA also offers a NAFA Foundation Programme, a one-year practice-based programme for Secondary 4 NA students who wish to pursue a creative arts diploma. UAS also offers postgraduate degree programmes in the creative arts of varying durations.
1.3. List of Higher Education Institutions
MOE oversees the following publicly-funded Institutes of Higher Learning (IHLs) and government-supported private university:
- Five Polytechnics – Nanyang Polytechnic, Ngee Ann Polytechnic, Republic Polytechnic, Singapore Polytechnic and Temasek Polytechnic;
- ITE;
- Six AUs – National University of Singapore (NUS), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore Management University (SMU), Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), Singapore Institute of Technology (SIT) and Singapore University of Social Sciences (SUSS); and
- UAS – Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts (NAFA) and LASELLE College of the Arts (LASELLE), as constituent colleges of UAS.
A list of higher education institutions and other post-secondary options can be found here: https://www.moe.gov.sg/post-secondary/overview
1.4. Number of Students in Higher Education
In 2023, there are over 81,000 students enrolled in the AUs, 61,000 students enrolled in the Polytechnics, 27,000 students enrolled in the ITE, and 5,000 students enrolled in UAS (accurate as of November 2024).
The statistics can be found in Singapore’ Education Statistics Digest 2024.
1.5. Structure of Academic Year
As the academic cycles differ across our IHLs, we have attached the individual IHLs’ academic calendars for AY 2025/26 below.
Polytechnics and ITE
The polytechnics have two semesters per academic year, with 13 to 15 teaching weeks and two to three examinations weeks per semester. ITE has two terms per academic year, with 18 teaching weeks and two examination weeks per term.
Polytechnics_Academic_Calendar_AY_25-26
ITE_Academic_Calendar_AY_25-26
Autonomous Universities (AUs)
The National University of Singapore (NUS), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore Management University (SMU) and Singapore University of Social Sciences (SUSS) have two semesters per academic year, with 12 to 13 teaching weeks and two to three examinations weeks per semester. The Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and Singapore Institute of Technology (SIT) have three trimesters per academic year, with 12 to 13 teaching weeks and one examination week per trimester.
NUS_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
NTU_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
SMU_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
SUTD_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
SIT_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
SUSS_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
University of the Arts Singapore (UAS)
LASELLE and NAFA (Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts) have two semesters per academic year, with 13 teaching weeks and two assessment weeks per semester. The NAFA Foundation Programme has three trimesters per academic year, with 8 to 13 teaching weeks and one examination week per trimester.
SIT_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
NAFA_Academic_Calendar_AY2526
1.6. National Qualifications Framework (or Similar)
Not applicable.
1.7. Learning Outcomes in Higher Education
Not applicable.
1.8. Admission Requirements to Higher Education
Polytechnics and ITE
The minimum entry requirements (MERs) for all applicants with foreign qualifications are aligned across the polytechnics. Among other requirements, these MERs stipulate that all applicants should attain a level of competency in English sufficient to cope with the academic rigour of the course. On top of this, the polytechnics may also administer additional entrance and aptitude tests to determine suitability for admission.
University of the Arts Singapore (UAS)
There are no standardised admission requirements for foreign students that are imposed at the national level. Instead, each university has autonomy to impose its own admissions requirements on foreign students, such as achieving a minimum score in the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) or Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) examinations.
University of the Arts Singapore (UAS)
The constituent colleges of UAS, LASALLE and NAFA have minimum academic requirements for diploma and degree programmes in addition to their discipline-specific aptitude tests. For the diploma programmes, international students are required to complete at least 10 years of formal education with good passes in a recognised national/international examination. A minimum English language proficiency of C6 at GCE ‘O’ Level or equivalent applies to all diploma programmes. At the degree level, applicants are expected to have completed GCE A-Levels, a diploma or international equivalent, with a pass at General Paper, or achieve a minimum score in the IELTS or TOEFL.
1.9. Grading System
Most of the IHLs adopt a Grade Point Average (GPA) system. However, the specifics of the GPA systems differ across institutions.
Polytechnics and ITE
Polytechnics and ITE adopt a system of grade point average (GPA) where the maximum GPA for a module is 4.0, corresponding to a grade A. The overall GPA for a student is computed based on the required (graded) modules taken by the student.
Autonomous Universities (AUs)
NUS, NTU, SUSS and SIT have similar grading methods. The maximum GPA is 5.0, corresponding to a grade A or A+ for a particular subject. SUTD uses the 5.0 grading system as well, but students with A+ are awarded a GPA of 5.3 instead of 5.0. For SMU, the highest GPA score attainable is 4.0.
University of the Arts Singapore (UAS)
The constituent colleges of UAS, LASALLE and NAFA, have similar grading methods. The maximum GPA is 5.0, corresponding to a grade A or A+ for a particular subject.
1.10. Tuition Fee System for International Students
Most IHLs adopt a cohort-based fee structure for its full-time programmes. Under the structure, students are informed of the tuition fees payable during admission and will remain unchanged for the entire duration of the course.
MOE provides substantial subsidies to Singaporean students enrolled in MOE-subsidised programmes in our publicly-funded IHLs and UAS. On top of the subsidies, MOE also provides means-tested Government bursaries to Singaporean students from lower-and-middle income families.
International students enrolled in MOE-subsidised full-time diploma programmes in polytechnics and AIs, and MOE-subsidised full-time degree programmes in AUs have the option to take up the MOE Tuition Grant Scheme to receive subsidy for their tertiary education. In return for the subsidy received, these international students are required to complete a service obligation by working in Singapore-based companies for three years upon graduation. Subsidised international students pay higher tuition fees than Singapore Citizen students. A small proportion of international students opt out of the Tuition Grant Scheme and thus pay full (i.e. non-subsidised) fees. International students pursuing an education in ITE and degree programmes in AIs are not eligible for any Government subsidies.
Table: Annual Subsidised Tuition Fees for full-time programmes at Publicly-Funded IHLs and UAS for Academic Year 2025
|
|
Singapore Citizens
|
Singapore Permanent Residents
|
International Students
|
|
|
ITE
|
Nitec
|
S$466
|
S$6,542
|
S$18,562.34
|
|
2-Year Higher Nitec
|
S$626
|
S$7,852
|
S$20,852.90
|
|
|
Technical Diplomas
|
S$3,036 – S$3,446
|
S$6,292 – S$7,132
|
Only Singapore Citizen and Permanent Resident students are accepted into the technical diploma programmes
|
|
|
Polytechnics
|
S$3,100
|
S$6,400
|
S$12,400
|
|
|
Autonomous Universities (Degree)
|
S$8,250 – S$36,100
|
S$11,550 – S$51,850
|
S$17,950 – S$89,100
|
|
|
LASELLE and NAFA (Diploma)
|
S$4,810 – S$7,890
|
S$7,360 – S$10,550
|
$S12,300 – S$26,000
|
|
|
UAS’s Constituent Colleges, LASALLE and NAFA (Degree)
|
S$8,650 – S$10,270
|
S$12,100 – S$14,350
|
S$29,800 – S$32,650
|
|
Notes:
- Miscellaneous fees may also apply for the above IHLs.
- All the above tuition fees are subsidised fees. International students enrolled in the Arts Institutions’ degree programmes pay non-subsidised fees.
- Subsidised fees for international students include Goods & Services Tax (GST).
1.11. Graduation Requirements and/or Qualification Awarding Requirements
Qualifications awarded by the IHLs range from Higher National ITE Certificates (HNitec) awarded by ITE to polytechnic diplomas and university degrees. The IHLs and UAS determine the graduation requirements for different types of qualifications awarded.
1.12. Relevant Current/Prospective Reforms in Higher Education
Not applicable.
Chapter 2: Quality Assurance in Higher Education
2.1. Quality Assurance Body in Higher Education
Once every six years, the publicly-funded IHLs and UAS undergo a quality assurance validation by an external review panel that is convened by the Ministry of Education. The validation involves an institutional self-assessment in focus areas such as governance, teaching and learning, a one-week visit by the external review panel, and follow-ups to be proposed by the institutions to address the external review panel’s findings and recommendations.
2.2. Quality Assurance System
|
|
Study programme
|
Institution
|
|
Voluntary
|
||
|
Compulsory
|
X | |
|
Regularity
|
|
Once every 6 years
|
|
External
|
X | |
|
Internal
|
2.3. Programme Authorisation and Quality Assurance
Not applicable.
Chapter 3: Credit System in Higher Education
3.1. Description of Credit System
The Institutes of Higher Learning (IHLs) each operate their own credit systems. In the case of credit transfers, the IHLs have the flexibility to set their credit transfer arrangements with the respective partners in question. This is to account for differing modes and mediums of instruction, academic calendars and types of modules, when evaluating the feasibility of such transfers.
3.2. Credit Transfer System(s)
Not applicable.
3.3. Additional Information
Not applicable.
3.4. Is Application of Credit System in Higher Education Institutions Mandatory?
Not applicable.
3.5. Number of Credits per Academic Year/Semester
Not applicable.
3.6. Number of Credits per Higher Education Cycle
Not applicable.
3.7. Description of Credit Unit
Not applicable.
3.8. Link between Learning Outcomes and Credits
Not applicable.